The History of First Paper, Before paper as we know it existed, people communicated through pictures and symbols carved into tree bark, painted on cave walls, and marked on papyrus or clay tablets. About 2,000 years ago, inventors in China took communication to the next level, crafting cloth sheets to record their drawings and writings. And paper, as we know it today, was born! Paper was first made in Lei-Yang, China by Ts’ai Lun, a Chinese court official. In all likelihood, Ts’ai mixed mulberry bark, hemp and rags with water, mashed it into pulp, pressed out the liquid and hung the thin mat to dry in the sun. During the 8th century, about 300 years after Ts’ai’s discovery, the secret traveled to the region that is now the Middle East. Yet, it took another 500 years for papermaking to enter Europe. One of the first paper mills was built in Spain, and soon, paper was being made at mills all across Europe.
Then, with paper easier to make, paper was used for printing important books, bibles, and legal documents. England began making large supplies of paper in the late 15th century and supplied the colonies with paper for many years.
Finally, in 1690, the first U.S. paper mill was built in Pennsylvania.
At first American paper mills used the Chinese method of shredding old rags and clothes into individual fibers to make paper. But, as the demand for paper grew, the mills changed to using fiber from trees because wood was less expensive and more abundant than cloth. Today, paper is made from trees grown in sustainably managed forests and from recycled paper. Recycling has always been a part of papermaking. When you recycle your used paper, paper mills will use it to make new notebook paper, paper grocery bags, cardboard boxes, envelopes, magazines, cartons, newspapers and other paper products.

The history of paper is inextricably linked with that of culture and science.
The spark that set off the invention of paper was simple but extremely significant.
Humans had an urgent need: to communicate certain information to each other in written form. The information had to be set on a lightweight and durable medium that was easily transportable. The invention of paper allowed papyrus and parchment to be replaced with a material that was easier and, with the advent of new production techniques, cheaper to make.
The arrival of digital media has perhaps obscured the fundamental role that paper has played in spreading knowledge: it should not be forgotten that, until a few decades ago, the dissemination of any idea required a sheet of paper.
It’s interesting to note that the first definition of paper provided by the Treccani children’s encyclopaedia in Italy is: “A material that is essential for spreading ideas in everyday life. Over the centuries, paper has made an enormous contribution to progress, from enabling citizen participation in democratic life to raising levels of knowledge and education.”
The history of paper has mirrored the evolution of human society over the centuries: from the dissemination of scientific and philosophical knowledge to the spread of education right up to the creation of the kind of political and historical consciousness which gave birth of the modern nation state.
The history of paper: Chinese origins
Historical sources credit the invention of paper to Cai Lun, a dignitary serving the imperial Chinese court who, in AD 105, began producing sheets of paper from scraps of old rags, tree bark and fishing nets. The Chinese guarded the secret of paper making jealously for many centuries until, in the 6th century, their invention was brought to Japan by Buddhist monk Dam Jing. The Japanese immediately learned papermaking techniques and began using pulp derived from mulberry bark to produce this precious material themselves.
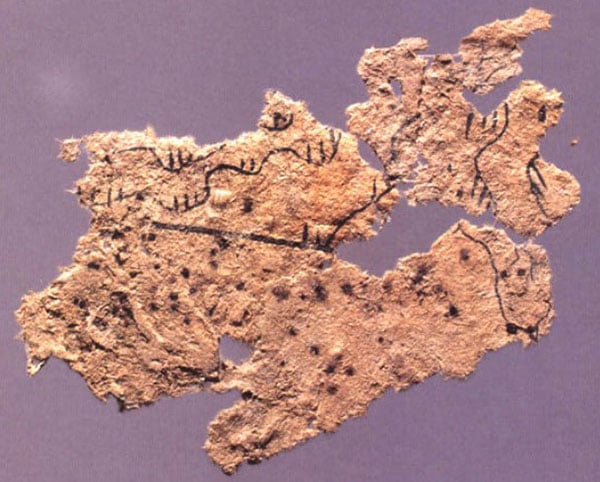

The history of paper: reaching the Arab world
The Arab world discovered the secrets of papermaking in AD 751, when the governor-general of the Caliphate of Bagdad captured two Chinese papermakers in Samarkand and, with their help, founded a paper mill in the Uzbek city. From here, aided by an abundance of hemp and linen, two high-quality raw materials perfect for making paper, production spread to other cities in Asia, particularly Baghdad and Damascus.
The process for making paper employed by the Arabs involved garnetting and macerating rags in water to obtain a homogenous pulp, which was then sifted to separate the macerated fibres from the water. The sheets thus obtained were subsequently pressed, dried and finally covered with a layer of rice starch to make them more receptive to ink. In the same period, people in Egypt and North Africa also started to make paper using the same techniques employed in the Arab world.
Paper reaches Europe
It wasn’t until the 11th century that paper arrived in Europe, with the Arab conquest of Sicily and Spain. However, paper was quickly considered an inferior-quality material compared to parchment, so much so that, in 1221, Holy Roman Emperor Frederick II prohibited its use for public documents. Rice starch, in fact, was an attractive food source for insects, which meant sheets of paper did not last long.
The history of paper owes much to the paper makers of Fabriano, a small town in the Marche region of Italy, who started producing paper using linen and hemp in the 12th century. By using new equipment and production techniques, these papermakers introduced important innovations:
- They mechanised rag grinding by using hydraulic hammer mills, significantly reducing the time it took to produce pulp.
- They started gluing sheets with gelatine, an additive that insects didn’t like.
- They created different paper types and formats.
- They invented watermarking.
Watermarking involved using metal wires to add decorations to paper which became visible when the sheet was held up to the light, allowing hallmarks, signatures, ecclesiastical emblems and other symbols to be inserted.

From the 14th century, papermaking began to spread to other European countries and, at the end of the 15th century, with the invention of movable-type printing, production really took off. The discovery of America and the subsequent European colonisation brought papermaking to the New World. Interestingly, in his book “Paper: Paging Through History”, Mark Kurlansky tells a curious anecdote: when the North American colonies rebelled, they boycotted all British goods, except the fine paper produced by London’s paper mills.
Paper as a means of mass communication
The industrial manufacture of paper began in the 19th century with the expansion of mass-circulation newspapers and the first best-selling novels, which required enormous quantities of cheap cellulose. In 1797, Louis Nicolas Robert created the first Fourdrinier machine, which was able to produce a 60-cm-long sheet. As demand for papermaking rags outstripped supply, alternative materials were sought, like wood pulp. With the development of new techniques for extracting fibres from trees, the price of paper fell dramatically, and paper soon became a product of mass consumption. In Britain alone, paper output soared from 96,000 tonnes a year in 1861 to 648,000 tonnes in 1900.
Once again, the history of paper and the history of humankind were closely intertwined: with the spread of cheap paper, books and newspapers became accessible to all, leading to an explosion of literacy among the middle classes. But it wasn’t until the turn of the century that paper would be employed for other uses, like toilet and wrapping paper, toys and interior decoration.
The environmental impact of paper and environmental choices
Paper manufacturing uses significant amounts of natural resources: between 2 and 2.5 tonnes of timber and 30-40 cubic metres of water are required to make one tonne of paper. What’s more, electricity and methane gas are needed to power the industrial machines used in the various production phases and, depending on the type of paper, a host of polluting chemical additives. That’s why, whenever possible, it’s important to choose sustainable or recycled paper to reduce the environmental impact of paper production.

Sustainable paper is made out of wood cellulose originating from Forest Stewardship Council-certified forests, where strict environmental, social and economic standards apply. Recycled paper, on the other hand, is made out of recovered paper. However, the chlorine used to bleach it, as well as other chemical additives used, mean that recycled paper is often not as environmentally friendly as commonly thought. To be sure that you are choosing a genuinely eco-friendly product, opt for paper with the Ecolabel certification, the European ecological quality label awarded to environmentally sustainable products.
Alternatives to paper
An excellent alternative to traditional paper is Crush paper, produced by venerable Italian papermakers Favini, made out of fruit and vegetable by-products. Production of this paper releases 20% fewer CO2 emissions and uses up to 15% less cellulose than traditional paper, and is suitable for many applications, from food and wine labels to premium-quality invitation cards, catalogues and brochures.

The latest innovation from Favini is Remake, paper made from 25% leather off-cuts, 40% recycled cellulose and 35% FSC-certified virgin cellulose fibres. It’s a fine-quality recyclable and compostable material, perfect for printing sophisticated publications and luxury packaging. Another great substitute is hemp, a highly durable material that has been used to make paper since ancient times, first by the Chinese and later by the Arabs. Cultivation of this plant does not require pesticides and provides a quantity of fibre per hectare that is 3-4 times greater than traditional forests. Its main drawback is the cost of processing hemp pulp, which is much higher than conventional cellulose extraction.
Our article on the history of paper finishes here, but we’re sure that, thanks to continued technical innovation, many more surprises lie ahead! The history of paper is far from over, and this fascinating and useful material will remain with us for years to come.






