Warfarin is a medication commonly prescribed as an anticoagulant (blood thinner). Here’s information about its uses, benefits, common symptoms, and potential side effects: Warfarin Tablet Uses Benefits and Symptoms Side Effects
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-to-know-about-warfarin-4178509-5c5dba3ac9e77c0001d92b14.png)
Uses and Benefits of Warfarin:
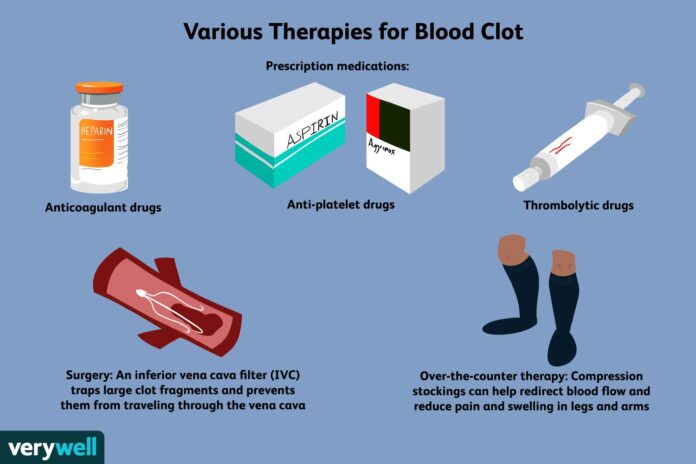
- Prevention and Treatment of Blood Clots: Warfarin is used to prevent and treat blood clots in conditions such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT), pulmonary embolism (PE), and atrial fibrillation. It works by inhibiting the synthesis of certain clotting factors in the liver, thereby reducing the ability of blood to clot.
Common Symptoms and Side Effects of Warfarin:
- Bleeding: One of the most significant side effects of warfarin is an increased risk of bleeding. This can manifest as bleeding gums, nosebleeds, bruising, prolonged bleeding from cuts, or blood in urine or stool. It’s important to promptly report any signs of bleeding to your healthcare provider.
- Purple Toe Syndrome: Rarely, warfarin can cause a condition called purple toe syndrome, characterized by purple or dark discoloration of the toes and feet due to small blood clots in the blood vessels.
- Skin Necrosis: In rare cases, warfarin can cause skin necrosis (death of skin tissue), usually occurring around areas of fat or muscle following a significant injury or surgery. This is more commonly seen when warfarin therapy is initiated without appropriate heparin bridging.
- Hair Loss: Some individuals may experience hair loss as a side effect of warfarin, although this is rare.
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: In rare cases, warfarin can cause allergic reactions characterized by symptoms such as rash, itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience any signs of an allergic reaction.
- Increased Risk of Bone Fractures: Long-term use of warfarin may be associated with a slightly increased risk of bone fractures.
- Purple, Blue, or Black Discoloration of the Skin: Some individuals may experience skin discoloration, such as purple, blue, or black spots or patches. This is usually harmless and resolves on its own.
It’s important to take
warfarin as prescribed by your healthcare professional and follow their instructions regarding the dosage and frequency of administration. Regular monitoring of blood clotting parameters, such as the international normalized ratio (INR), is necessary to ensure appropriate anticoagulation.
Inform your healthcare
provider about any pre-existing medical conditions, medications, or supplements you are taking to ensure the appropriate use of warfarin. Dietary considerations, especially vitamin K intake, may be important when taking warfarin due to its effect on blood clotting.
If you have any concerns or experience
troubling side effects while taking warfarin, consult with your healthcare provider for further evaluation and guidance. Regular monitoring and follow-up visits with your healthcare provider are typically recommended during warfarin treatment.
Warfarin Tablet Uses Benefits and Symptoms Side Effects